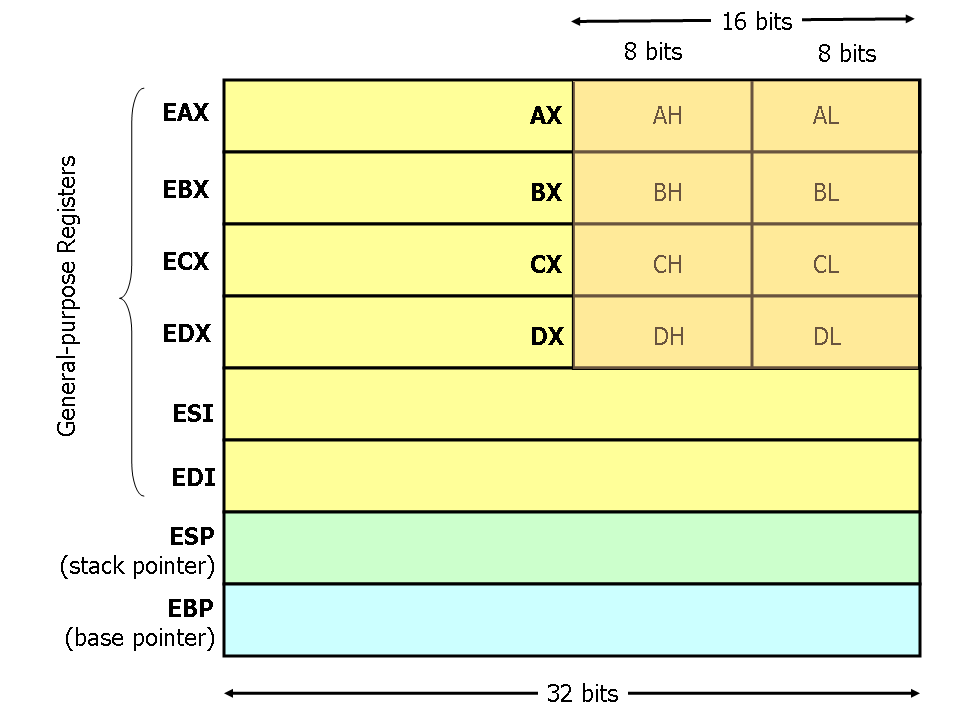
REGISTERS
Register Types
| Register | Description |
EAX | Accumulator, used for multiplication and division. |
EBX, EDX | General-purpose registers. |
ESI, EDI | High-speed memory transfer registers. |
ECX | Loop counter register. |
ESP | Stack pointer, points to the next available location in stack memory. |
EBP | Base pointer, used to reference function parameters and local variables on the stack. |
XMM0 [0-15] | Floating-point registers. |
EIP | Instruction pointer, points to the address of the next instruction to execute. |
EFLAGS | Flags register indicating the status of an operation. |
I can check more register types and information here.
Register Size
| Register | Size |
EAX | 32 bits |
AX | 16 bits |
AH, AL | 8 bits |
- x86 Registers, each register is 32 bits in size.
- Registers like
EAX, EBX, ECX, and EDX are standard, with the E denoting extended access to all 32 bits. - Dropping the
E to access only 16 bits (e.g., AX, BX, CX, DX). - Can also access 8-bit high and 8-bit low bytes (e.g.,
AH, BH, CH, DH and AL, BL, CL, DL).